Java for Beginners
September 16th, 2023
Week 2: Classes and Objects
Class 3: Introduction to Classes and Objects
Understanding Classes and Objects
In Week 1, we introduced you to the basics of Java programming. Now, in Week 2, we’ll dive deeper into the core of Java - classes and objects. Understanding classes and objects is fundamental to object-oriented programming (OOP).
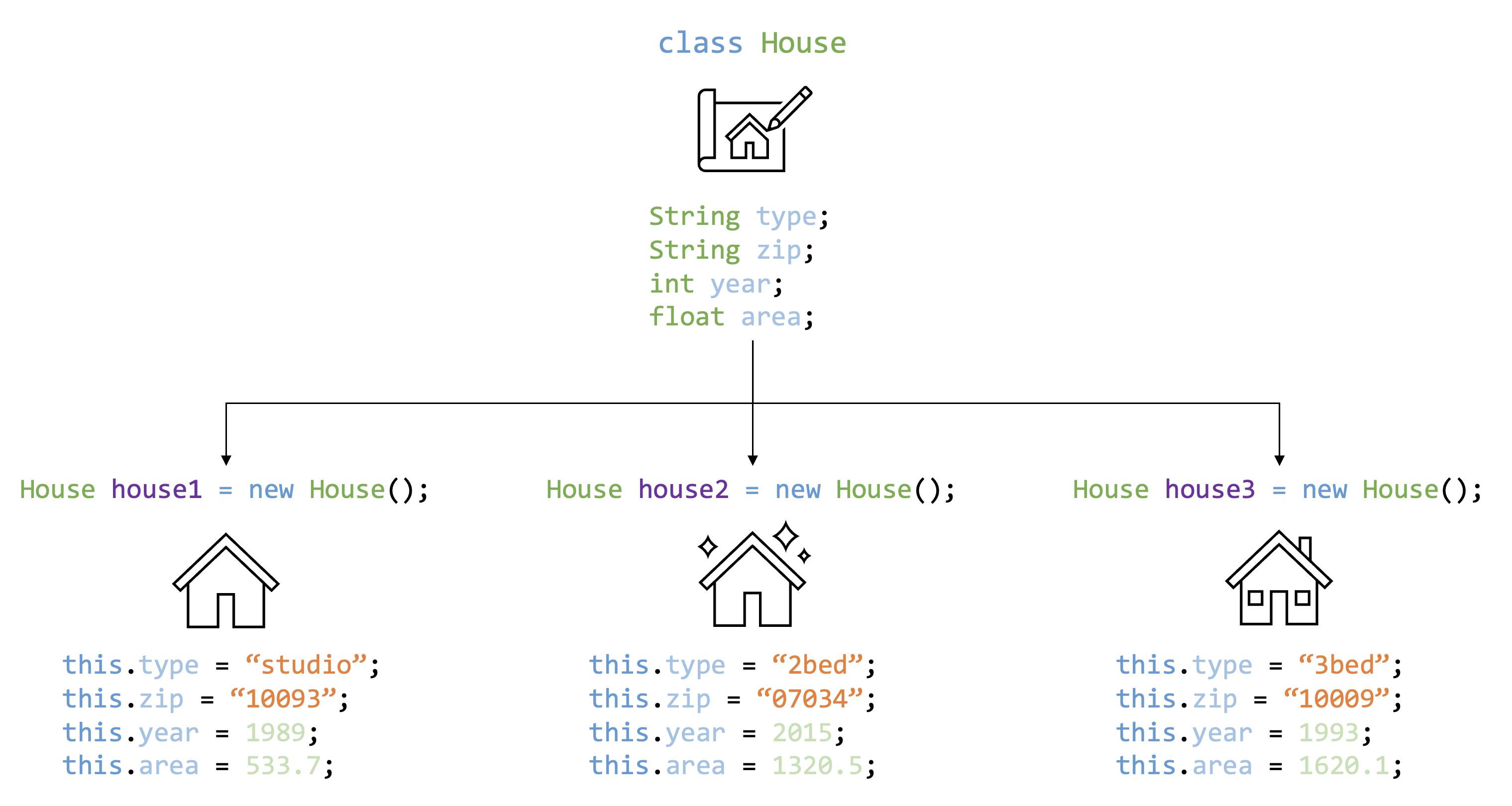
What is a Class?
- A class is like a blueprint or template for creating objects.
- It defines the structure and behavior of objects that will be created based on it.
- A class encapsulates data (attributes) and behavior (methods) that objects of that class will have.
What is an Object?
- An object is an instance of a class.
- Objects are created based on the class blueprint.
- Each object has its own unique data and can perform actions defined in the class.
Creating Custom Classes
Now, let’s see how to create our own classes in Java.
public class Car {
// Instance variables (attributes)
String brand;
String model;
int year;
// Constructor
public Car(String brand, String model, int year) {
this.brand = brand;
this.model = model;
this.year = year;
}
// Method to display car information
public void displayInfo() {
System.out.println("Brand: " + brand);
System.out.println("Model: " + model);
System.out.println("Year: " + year);
}
}
In this example, we’ve defined a Car class with attributes (brand, model, year) and a constructor to initialize these attributes. We also have a displayInfo method to print car information.
Creating Objects
Let’s create objects of the Car class:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating car objects
Car car1 = new Car("Toyota", "Camry", 2022);
Car car2 = new Car("Honda", "Civic", 2021);
// Calling the displayInfo method
car1.displayInfo();
car2.displayInfo();
}
}
In this example, we’ve created two Car objects (car1 and car2) and called the displayInfo method to display their information.
Instance Variables and Methods
- Instance variables (attributes) store data specific to each object.
- Methods define the behavior of objects.
Accessing Instance Variables and Methods
You can access instance variables and methods using the dot notation:
car1.brand = "Ford"; // Updating the brand attribute
car1.displayInfo(); // Calling the displayInfo method
Pop Quiz
Quiz 1: What is the purpose of a class in Java?
- To define a method in Java.
- To store and manage data during program execution.
- To initialize the attributes of an object when it is created.
- To create an instance of a class.
Quiz 2: What is an object in Java?
- A blueprint or template for creating classes.
- An instance of a class.
- A method that initializes class attributes.
- An access modifier for class members.
Quiz 3: What is the purpose of a constructor in Java?
- To define a class in Java.
- To create an instance of a class.
- To initialize the attributes of an object when it is created.
- To perform mathematical calculations in Java programs.
Quiz 4: Which of the following is NOT an example of an instance variable in a class?
- The number of objects created from the class.
- The class's name.
- The height of a person (in a class representing people).
- The name of a book (in a class representing books).
Quiz 5: How is an object different from a class in Java?
- An object is a blueprint for creating classes.
- An object is an instance of a class.
- An object is used to define methods in Java.
- An object is a data type in Java.
Answers:
- B
- B
- C
- B
- B
Homework
- Create a class named
Studentwith attributesname,age, andmajor. Include a constructor and a method to display student information. - Create two
Studentobjects and display their information.
Class 4: Constructors, Access Modifiers, and Method Overloading
Class Inheritance Class inheritance in Java allows you to create a new class (subclass or child class) that inherits attributes and behaviors from an existing class (superclass or parent class). Subclasses can extend and specialize the functionality of the superclass, promoting code reusability and creating a hierarchical relationship between classes.

Constructors
In the previous class, we learned about creating custom classes and objects. Now, let’s explore constructors, access modifiers, and method overloading to enhance our understanding of classes and objects.
What is a Constructor?
- A constructor is a special method that is called when an object is created.
- It is used to initialize the object’s attributes and perform any setup needed.
Default Constructor
If you don’t provide a constructor for your class, Java automatically provides a default constructor with no arguments. However, you can create your own constructors to customize object initialization.
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
// Default constructor
public Student() {
name = "Unknown";
age = 0;
}
}
Parameterized Constructor
You can create parameterized constructors to allow for custom initialization when creating objects.
public class Student {
String name;
int age;
// Parameterized constructor
public Student(String n, int a) {
name = n;
age = a;
}
}
Access Modifiers
Access modifiers control the visibility and accessibility of class members (attributes and methods). There are four types of access modifiers in Java:
- public: The member is accessible from any other class.
- private: The member is only accessible within the same class.
- protected: The member is accessible within the same class and its subclasses.
- default (no modifier): The member is accessible only within the same package.
public class Person {
public String name;
private int age;
protected String address;
String email; // Default access modifier
}
Method Overloading
Method overloading allows a class to have multiple methods with the same name but different parameters. The compiler determines which method to call based on the number and types of arguments.
public class Calculator {
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
public double add(double a, double b) {
return a + b;
}
}
In this example, we have two add methods—one for integers and one for doubles. Java will choose the appropriate method based on the argument types.
Pop Quiz
Quiz 1: What is the default access modifier for class members in Java if no modifier is specified?
- public
- private
- protected
- default (package-private)
Quiz 2: Which access modifier allows a class member to be accessible only within the same class?
- public
- private
- protected
- default (package-private)
Quiz 3: What is method overloading in Java?
- It is a way to create multiple copies of a method within the same class.
- It allows a method to have multiple names.
- It allows a class to have multiple constructors with the same parameters.
- It allows a class to have multiple methods with the same name but different parameters.
Quiz 4: Which keyword is used to call a constructor of the superclass in Java?
- super
- this
- extends
- inherits
Quiz 5: What is the purpose of a parameterized constructor in Java?
- To define a class in Java.
- To create an instance of a class.
- To initialize the attributes of an object when it is created.
- To perform mathematical calculations in Java programs.
Answers:
- D
- B
- D
- A
- C
Homework
- Create a class named
Bookwith attributestitle,author, andyear. Include both default and parameterized constructors. Also, create a method to display book information. - Overload the method to display book information so that it can handle books with or without an author.
That’s it for Class 4! Next, we’ll explore more advanced concepts, including inheritance and polymorphism.
